Introduction to Generative AI - A Beginner's Guide
This article explains Generative AI (GenAI) in simple terms for beginners. Learn what GenAI is, how it works, the difference between building models and using them, and the key concepts behind popular models like GPT.
Generative AI Introduction
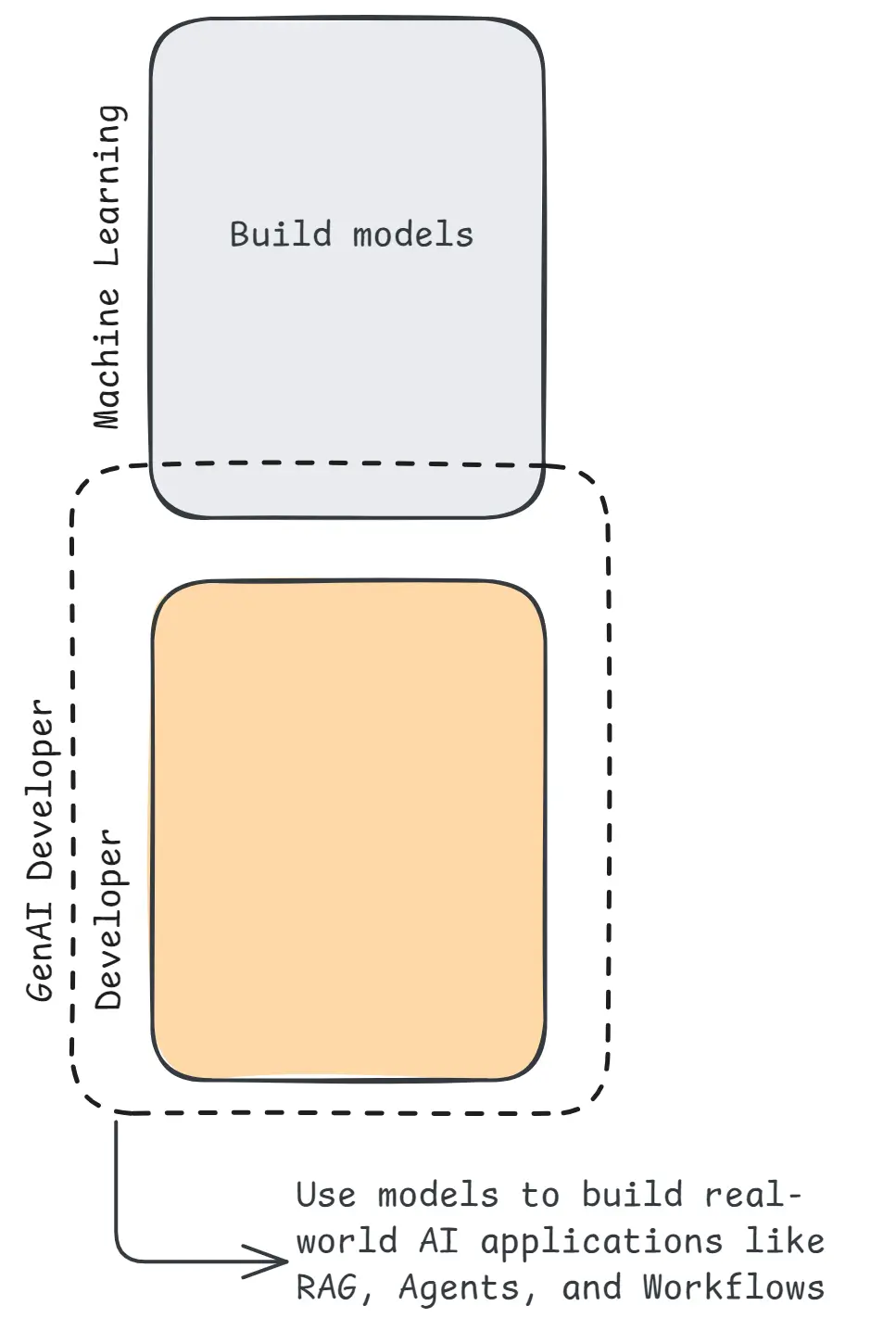
1. Do We Need to Learn Mathematics for GenAI?
If you want to build AI models, then yes, you need deep math, statistics, and neural network theory.
But if you're a developer who wants to build AI-powered apps, agents, workflows, and real-world solutions, then:
No, you don’t need advanced mathematics.
You only need a basic understanding of how models work (1%), not the complex math behind them.
GenAI vs ML Models
ML Engineers
- Create and train models and build the models
- Work on neural network code
- Use heavy maths & statistics
Developers (You)
- Use existing AI models
- Build products & automations
- Solve real-world problems
- Make money by deploying solutions
So developers don’t need deep ML math, they need problem-solving skills, tools & workflows.
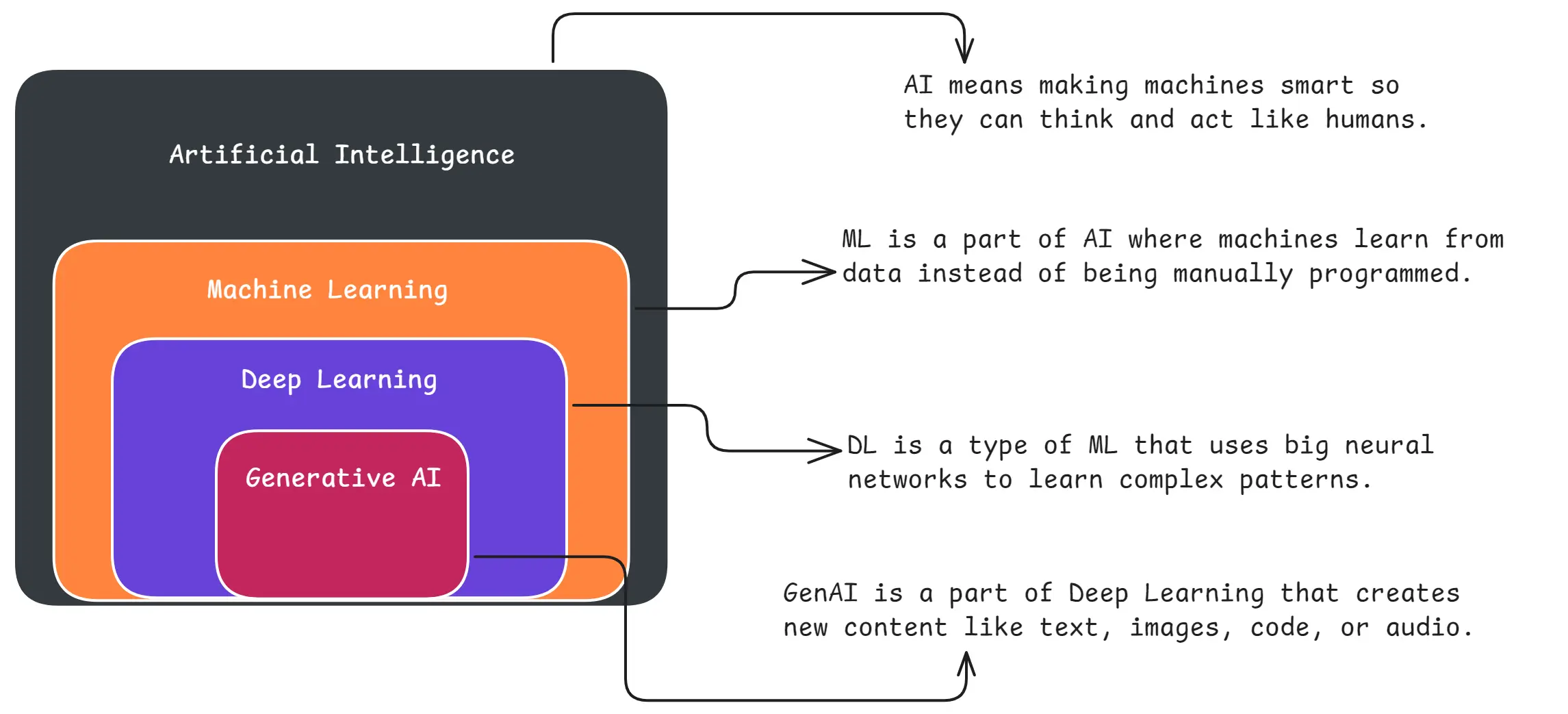
2. What is Generative AI?
What is GenAI
GenAI (Generative AI) refers to AI systems that can create new content like text, images, videos, code, audio, etc.
Examples: ChatGPT, Midjourney, Claude, Gemini.
3. What Is GPT by OpenAI?

What is GPT
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is a large language model created by OpenAI that can:
- Understand text
- Generate text
- Reason, solve problems
- Perform tasks using tools
It is built using the Transformer architecture.
Generative
Nature: It’s a creator model that generates new content - like text, code, answers, stories, images, and more.
Pre-trained
It is already trained on a huge amount of data before you use it.
Transformer
It predicts the next word by looking at all previous words and choosing the most likely token.
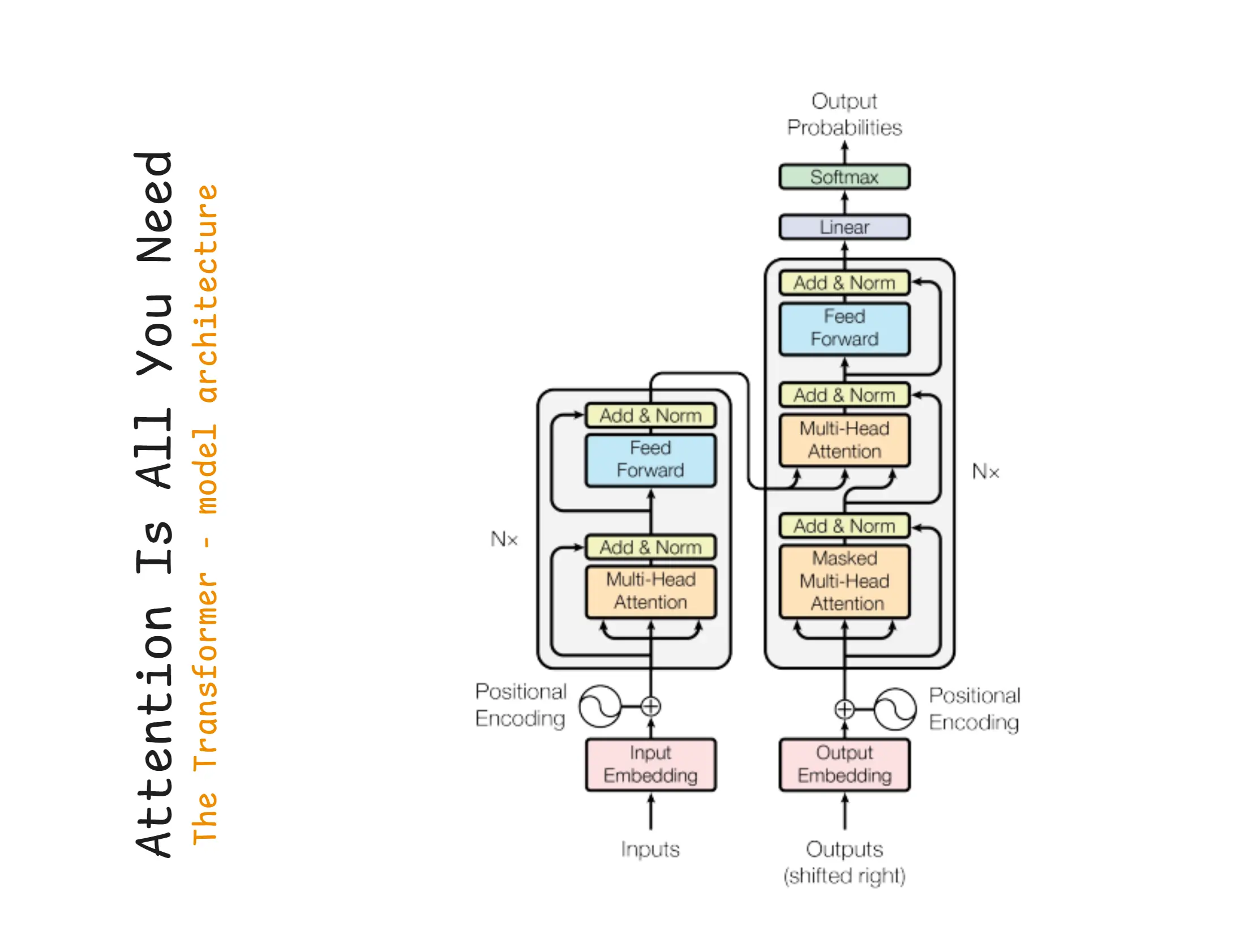
4. Google Article on "Attention Is All You Need"
Google Research Paper: Attention Is All You Need
This 2017 paper introduced a new AI model called the Transformer that understands which words in a sentence are important using a method called attention instead of older methods like RNNs (Recurrent Neural Network) or LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory).
This one paper is the reason today’s Generative AI boom (like GPT, ChatGPT, Gemini) became possible.
Attention Is All You Need
What Are RNNs and LSTMs? (Super Simple)
RNN (Recurrent Neural Network)
- Reads a sentence one word at a time.
- Tries to remember past words but forgets quickly.
- Works for small sentences but struggles with long ones.
- Slow because it processes words step-by-step.
Think of RNN like: Reading a paragraph but forgetting the earlier lines as you move forward.
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory)
- A better version of RNN.
- Has a stronger memory so it remembers more of the sentence.
- Still reads things one by one, so it's slow.
- Still not good at very long sentences or big context.
Think of LSTM like: Reading a paragraph with slightly better memory, but still forgetting some details after a while.
5. What Is a Transformer and How Does It Predicts the Next Word?
Transformers read all words in a sentence at the same time and use attention to figure out which words are important for predicting the next word.
What Is a Transformer?
A Transformer is a modern AI model that can understand and generate text by looking at all the words in a sentence at the same time using a technique called attention to find out which words are important.
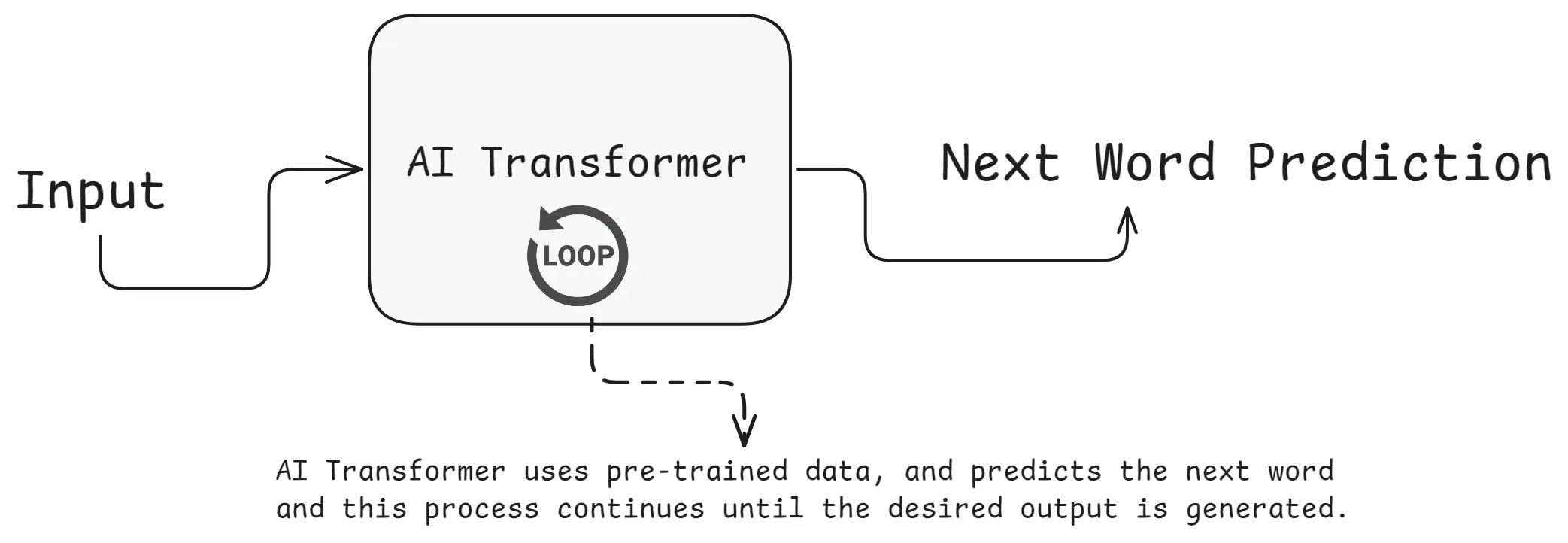
What is a Transformer
A Transformer is an AI architecture that processes input, uses pre-trained data, and predicts the next word or output based on context, this process continues until the desired or suitable output is generated.
How Does It Predict the Next Word?
- It reads all the previous words together.
- It finds which words are important using attention.
- It calculates probabilities for the next word.
- It selects the most likely next word (token).
- It repeats this process until the complete output is finished.
Example: Let's suppose you want number 4
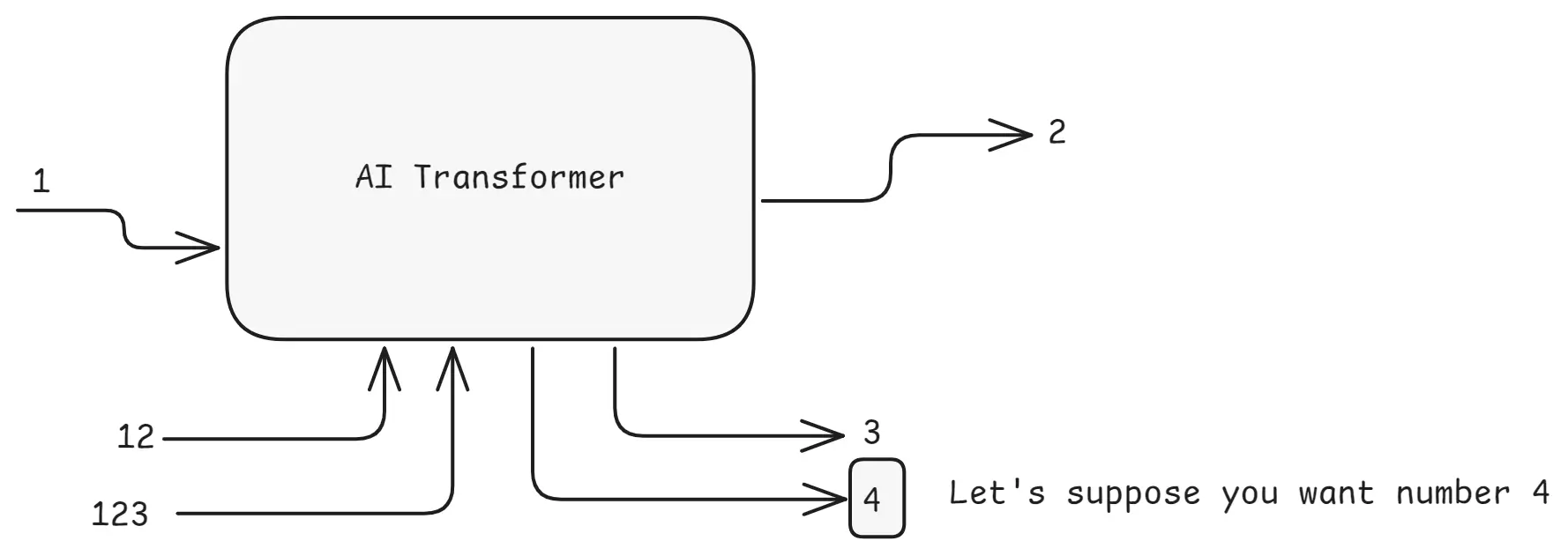
Transformer Example
Example: Let's suppose AI model gives final word "Heyy"
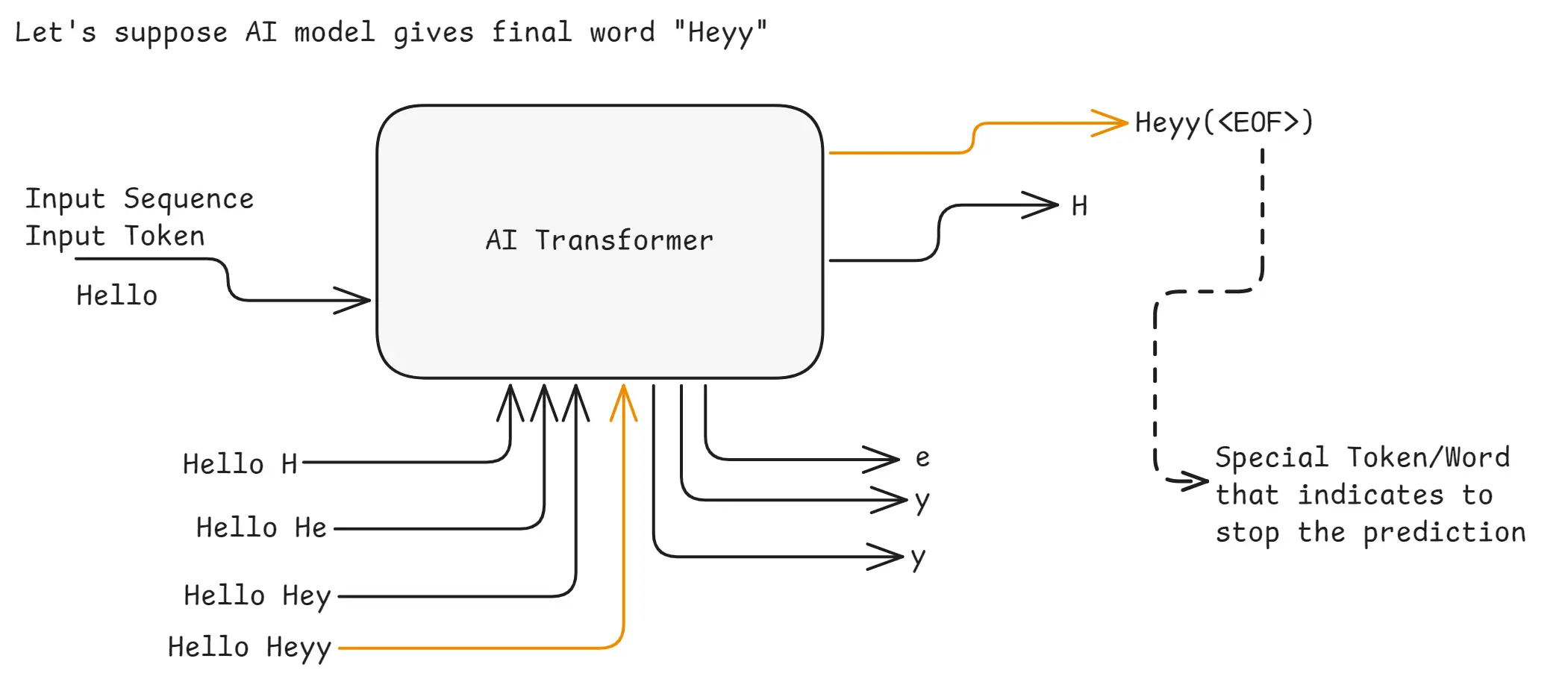
Transformer Example 2
6. How GPT Generates the Next Word?
GPT creates text one token (word or part of a word) at a time.
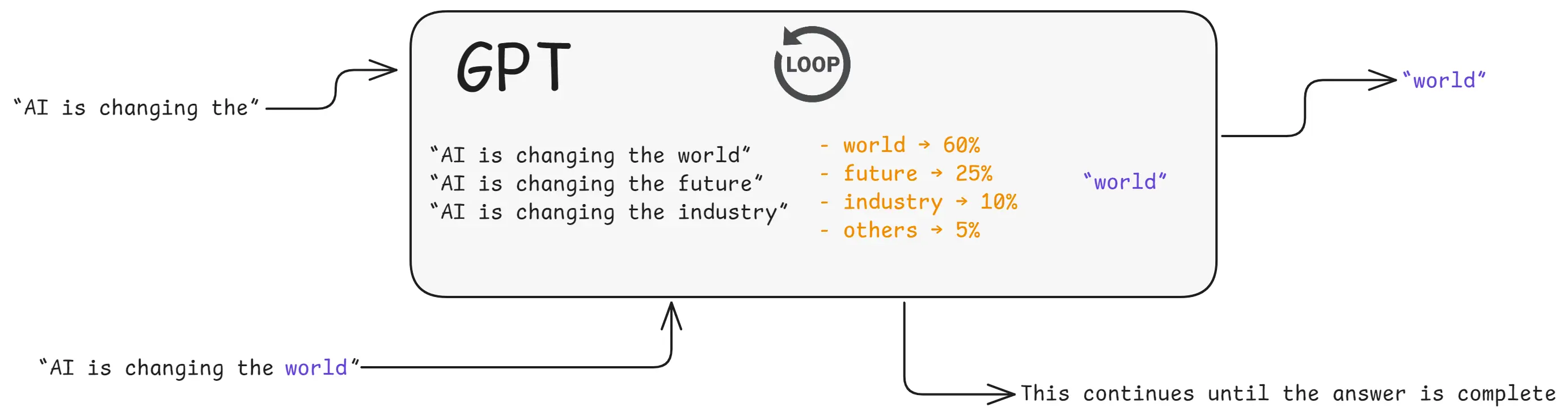
How GPT Generates Next Word
Here’s how it decides what comes next:
1. You give GPT some text
Example: “AI is changing the”
2. GPT converts the text into tokens (numbers)
It understands numbers, not words. “We will understand later in detailed”
3. It looks at all previous tokens together
Using attention, it checks which words matter most.
4. It uses patterns learned during training
GPT has seen billions of examples, so it knows common patterns like:
“AI is changing the world”
“AI is changing the future”
“AI is changing the industry”
5. It calculates probabilities for the next word
Example:
- world → 60%
- future → 25%
- industry → 10%
- others → 5%
6. It picks the most suitable next word
Usually: “world”
7. It adds that word and repeats
Now GPT predicts the next word again… and again…
This continues until the answer is complete.
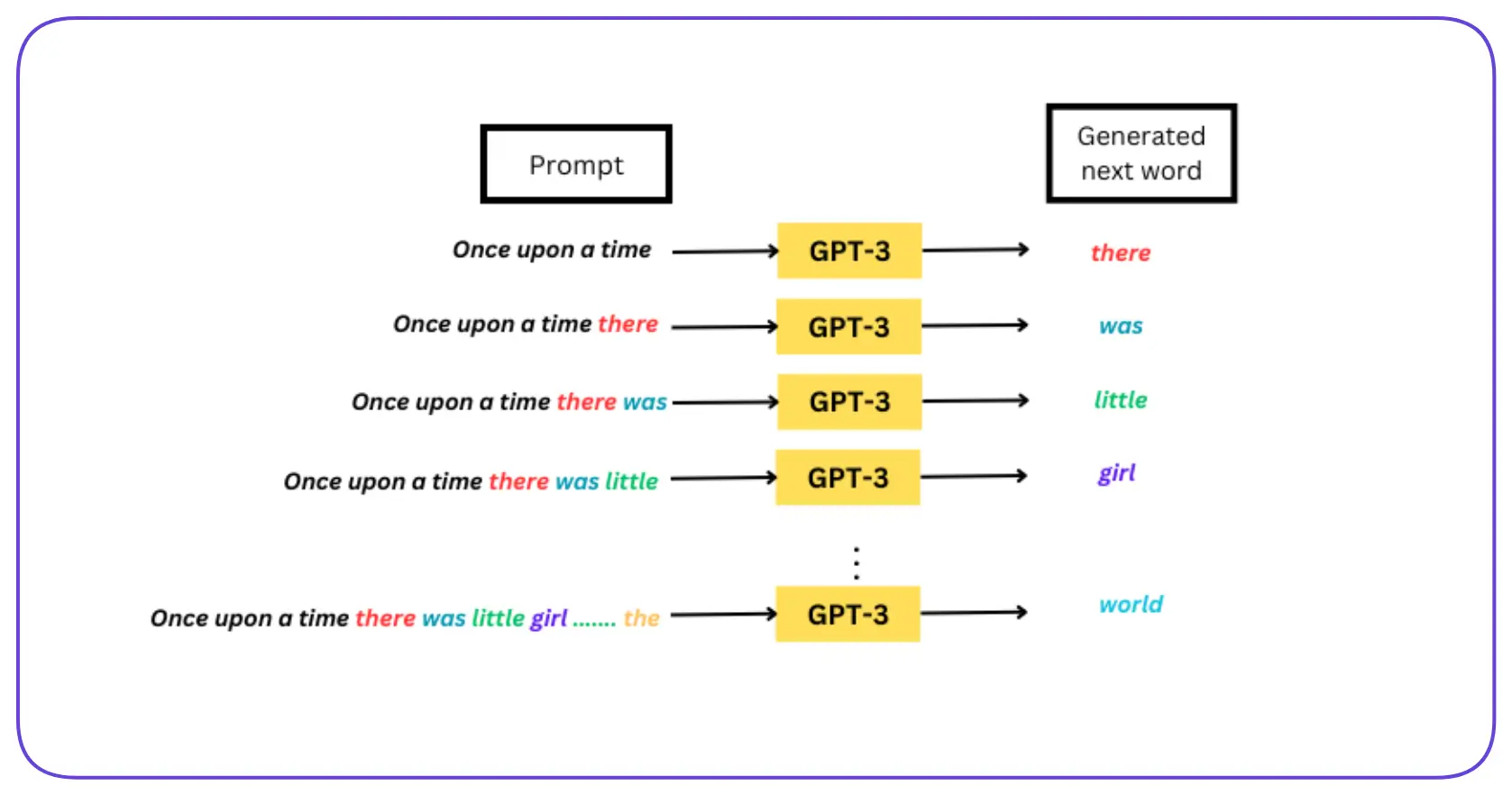
GPT Next Word Prediction
GPT predicts the next word by checking the context, calculating probabilities, and choosing the most likely token repeating this until the whole response is generated.
7. What Are Input Tokens & Input Sequence?
What Are Input Tokens?
Input tokens are small pieces of text (words, subwords, or characters) that the model can understand because AI models can’t read full sentences directly, they first break text into tokens.
Example:
Text: *“I love coding”*Tokens: **[“I”, “love”, “cod”, “ing”]**In simple words: Tokens means the building blocks of text that GPT reads.
What Is an Input Sequence?
An input sequence is the ordered list of tokens given to the model. It’s the full line of tokens arranged in the correct order.
Example:
“I love coding” → tokens → **[I, love, cod, ing] //** This entire list is the *input sequence*.In simple words: Input sequence means all tokens together, in order, as the model reads them.
8. What Are Vocabulary, Encoding & Decoding, and an AI Model?
What Is Vocabulary?
Vocabulary is the full set of tokens an AI model knows. It’s like a dictionary of all words, subwords, symbols, and characters the model can understand.
What Is Encoding?
Encoding is the process of converting text → tokens → numbers so the model can understand it.
What Is Decoding?
Decoding is the opposite: converting numbers → tokens → human text.
What Is an AI Model?
An AI model is a trained mathematical system that takes input, understands it, and produces meaningful output (text, image, etc.).
Vocabulary: The complete list of tokens (words/subwords) an AI model knows. Encoding: Converting text into numbers so the model can understand it. Decoding: Converting numbers back into readable text. AI Model: The trained system that processes input and generates output.
9. A Deep Dive into Transformer Architecture
Understanding How Transformers Work: A Deep Dive into Transformer Architecture
Transformer Architecture
1. What Is a Transformer?
A Transformer is a type of neural network model designed to process sequences (like text) by looking at all parts of the sequence at once and learning which parts matter using attention. It’s the core architecture behind modern GenAI models like GPT.

Transformer Architecture
2. What Is Transformer Architecture?
Transformer architecture is the layered design that combines: token embeddings, positional information, repeated blocks of self-attention and feed-forward networks, plus normalization and residual connections. It processes tokens in parallel and learns relationships between tokens via attention heads.

Transformer Architecture Layers
3. What Are Encoding and Decoding?
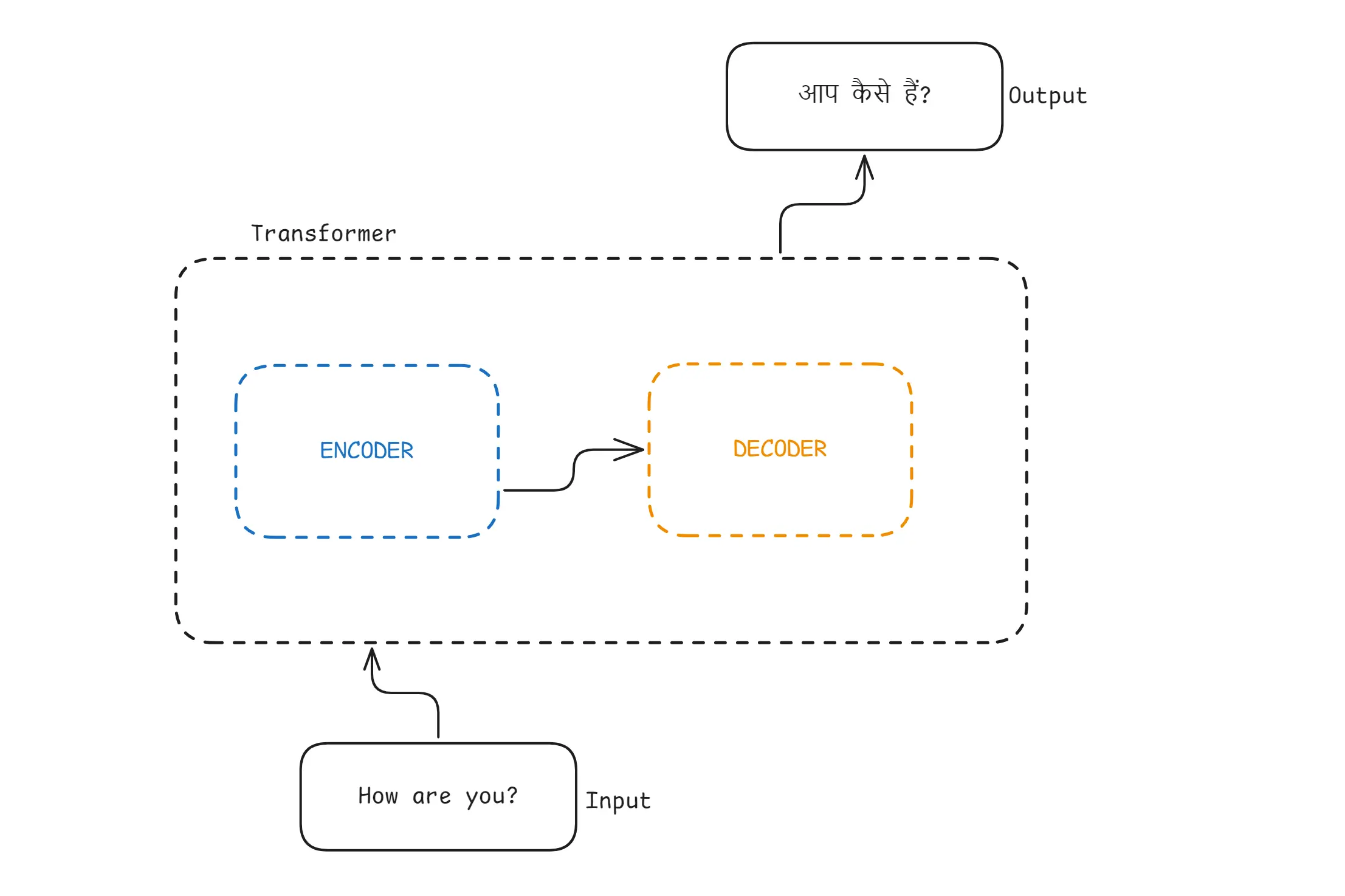
Transformer Encoding Decoding
Encoding is the process where the Transformer’s encoder reads the input sentence, understands its meaning, and converts it into a matrix of numerical representations.
For example, if the input is: “How are you?”The encoder transforms this sentence into a rich vector-based representation that captures the meaning, context, and relationships between words.
Decoding is the process where the Transformer’s decoder takes that encoded representation and generates the output step-by-step.
For example output is: “आप कैसे हैं?”In a translation task, the decoder uses the encoded information to produce the next language token at a time until the full output is complete.
In Simple Words:
- Encoder means understands the input
- Decoder means produces the output
- They work together to convert one sequence into another.
4. What Is a Tokenization?
Tokenization is the process of breaking raw text into smaller pieces called tokens (words, subwords, or characters) and mapping each token to a numeric ID the model can process.
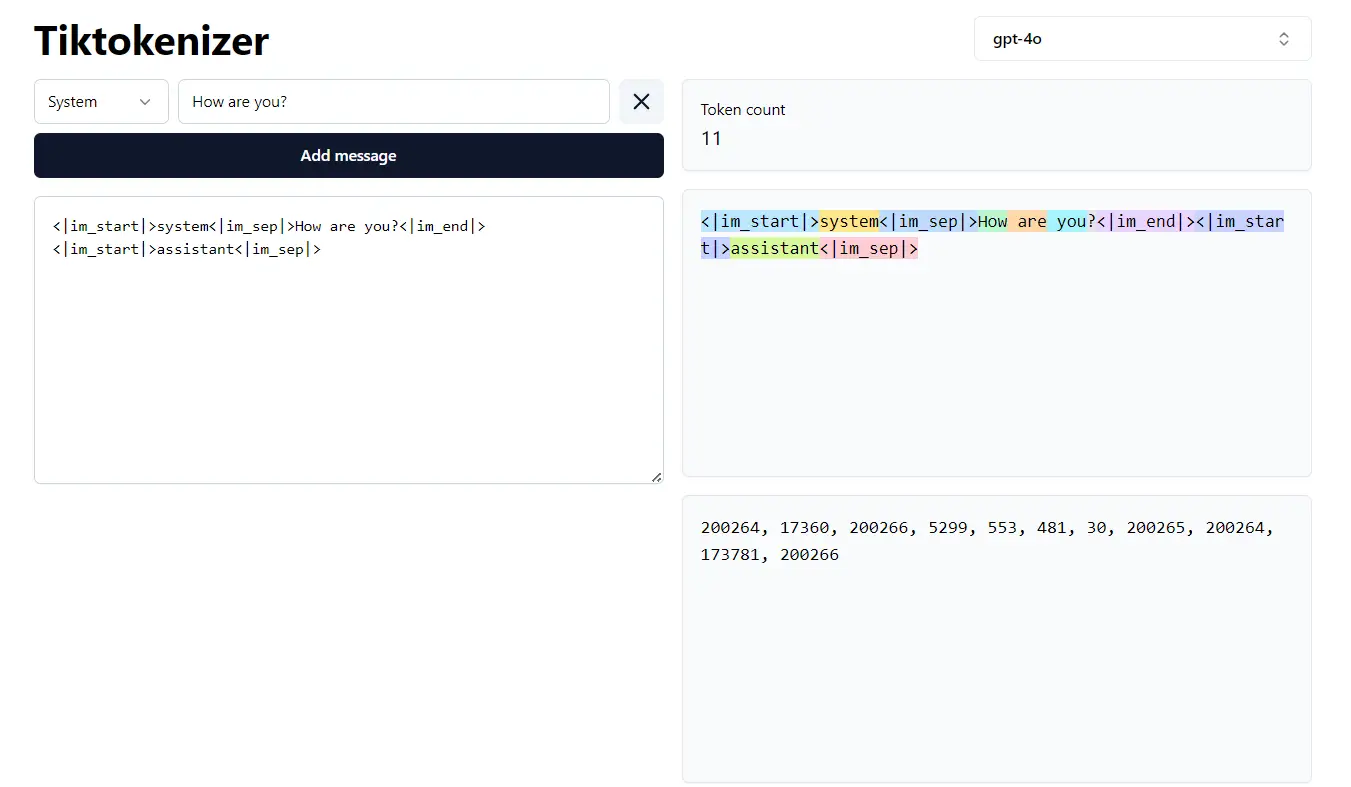
What is Tokenization
Explore this tool for tokenization: Tiktokenizer and OpenAI Platform.
Try to understand the tokenization:
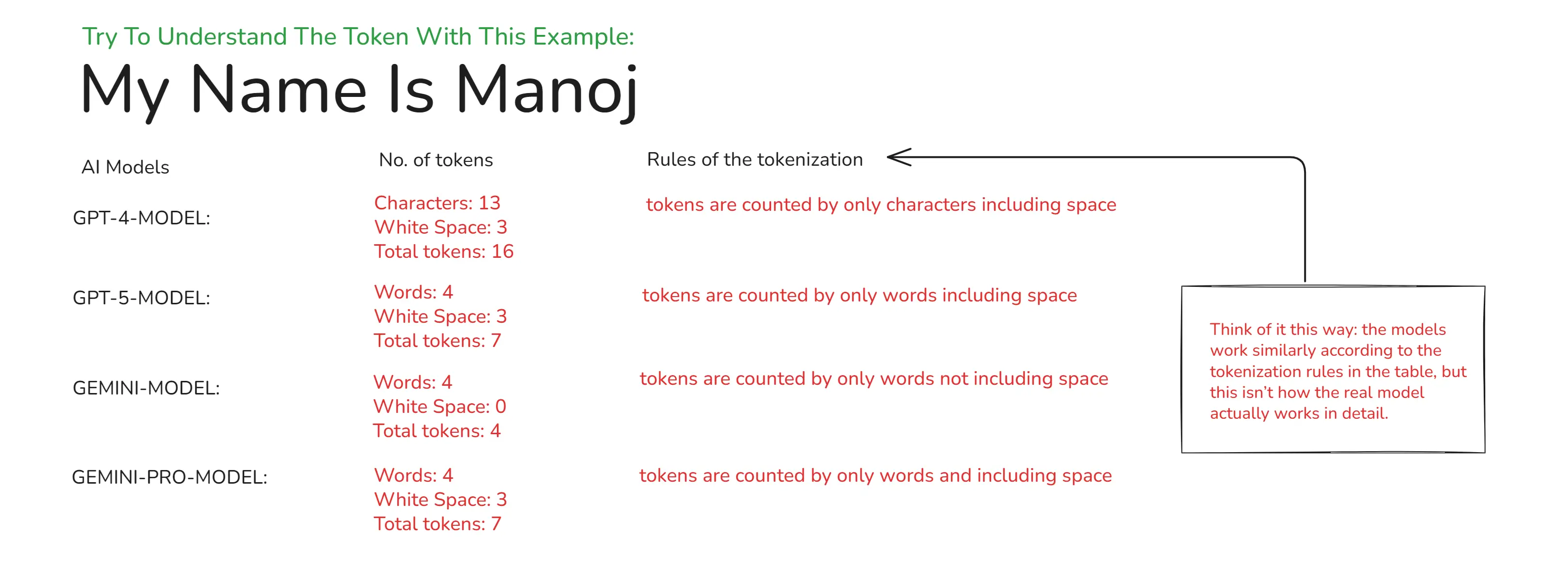
Tokenization Example
Try to code for better understanding of tokenization:
Build a custom tokenizer in JavaScript that learns vocab from text, supports ENCODE/DECODE and handles special tokens. The final output can be showcased in various formats:
- Website
- CLI Tool
- Package or
- API
Understanding the topics for building this project Custom Tokenizer:
- What is Token
- Tokenizer Rule
- Encoding & Decoding
- Vocab (Vocabulary) learning
- Special tokens, Like <PAD>, <UNK>, <START>, <END>, <EOS>, <BOS> etc.
Building this using NPM package or own logic:
1. https://www.npmjs.com/package/js-tiktoken
2. https://github.com/BCAPATHSHALA/custom-tokenizer5. What Are the Transformer Phases?
Training Phase (Learning Stage)
The model learns from large amounts of text, finds patterns, and updates its internal weights so it becomes smarter.
- The model learns from huge amounts of text.
- It predicts the next word and checks if it was right or wrong.
- It updates its internal weights after every mistake to improve accuracy.
- Training requires powerful hardware and takes a long time.
- This is where the model “learns everything.”
Inference Phase (Using Stage)
The already-trained model uses what it learned to predict the next words and generate responses for the user.
- The trained model is used to generate answers for users.
- It does not learn anymore; it only uses what it already knows.
- It reads your input, predicts the next word, and continues until the response is complete.
- This phase is fast and happens in real time.
- This is where the model “uses what it learned.”
6. What Are Weights in AI / Transformers?
- Weights are the internal values inside the model that decide how important each piece of information is.
- They control how the model learns patterns, relationships, and meaning in data.
- During training, the model updates its weights whenever it makes a mistake, so it becomes more accurate.
- After training, the weights are fixed and used during inference to generate correct outputs.
Simple Example:
If the model sees the sentence: "The sky is ___" The weights help it decide which word is most likely next (e.g., blue).
Conclusion
Generative AI is a powerful technology that enables machines to create human-like content. As a developer, you don’t need deep mathematics to build AI-powered applications. Understanding the basics of how models like GPT work, including concepts like tokens, transformers, attention, and the training/inference phases, will empower you to leverage AI effectively in your projects.
Happy Learning and Building with Generative AI!