Master Prompt Engineering for Generative AI: A Beginner's Guide to Communicating with LLMs
Master Prompt Engineering is the foundation skill behind all Generative AI development. It teaches you how to communicate with LLMs in a way that gives accurate, structured, and reliable outputs.

Master Prompt Engineering
1. Introduction to Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering is a skill that allows you to communicate with LLMs (Large Language Models) in a way that gives accurate, structured, and reliable outputs.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt Engineering means giving clear and correct instructions to Large Language Models (LLMs) so they understand your goal and produce the output you want.
Think of it like talking to a very smart person:
- If you ask the question clearly, you get a good answer
- If you ask a confusing question, you get a confusing answer
LLMs (like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini) work the same way. It is similar to writing a “program” using natural language instead of code.
Example:
Bad prompt: “Write something about marketing.”
Good prompt: “You are a digital marketing expert. Explain social media marketing in simple words with 3 examples.”Why Prompt Engineering is Important
Prompt Engineering is important because the quality of your instructions directly decides the quality of the AI’s output. When your prompt is clear, structured, and specific, the model gives accurate and helpful responses.
Key Reasons
-
LLMs follow your instructions exactly:
If your prompt is unclear, the model will also give unclear or confusing answers.
-
Better prompts is equals to better results:
A well-written prompt produces clean, structured, and useful output.
-
Reduces AI mistakes (hallucinations):
Clear instructions help the model avoid giving wrong or made-up information.
-
Essential for building chatbots, agents, and RAG systems:
These AI systems rely heavily on precise prompting to work correctly.
-
Saves tokens and cost:
Good prompts reduce long, irrelevant, and repetitive responses.
-
Foundation for advanced AI workflows:
Skills like LangGraph, Agent SDK, and automation require strong prompting ability.
Example:
Weak prompt: “Explain DevOps.”
Strong prompt: “You are a DevOps instructor. Explain DevOps in simple words using 5 short points and give one real-world example.”2. What is GIGO in AI?
GIGO stands for “Garbage In, Garbage Out.”
This means that if you give the AI a bad, unclear, or wrong word and prompt, the output will also be bad, unclear, or wrong.
AI models do not magically fix wrong inputs they follow whatever you give them.
Why GIGO Matters in AI
-
Poor instructions is equals to poor output
If the prompt is confusing, the AI will also produce confusing results.
-
AI cannot guess your intention
It only sees the words you provide, not what you “meant.”
-
Quality of output depends on quality of input
Good input = good output.
Bad input = useless output.
-
Helps reduce mistakes and hallucinations
Clear prompts guide the model better.
Example:
Bad Input (Garbage In): “Write code for something cool.”
AI Output (Garbage Out): Random or irrelevant code, not useful.Good Input (Clear Input): “Write a Node.js function that takes an array of numbers
and returns the sum. Keep the code simple and beginner-friendly.”AI Output (Clear Output):
function sumArray(numbers) {
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
total += numbers[i];
}
return total;
}
// Example usage:
const myNumbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(sumArray(myNumbers)); // Output: 153. What Is Prompting?
Prompting is the process of giving instructions, questions, or examples to an AI system like ChatGPT to guide it in producing a desired response. A prompt is the input you provide, and the AI uses that input to understand what you want and generate an appropriate output.
Prompting can be as simple as asking a question (“What’s the weather like today?”) or as detailed as giving step-by-step instructions (“Write a friendly email reminding my coworker about tomorrow’s meeting.”).
Good prompting helps the AI understand:
- What you want
- How you want it delivered
- What style or format it should use
In short, prompting is how you “communicate” with an AI to get the best and most accurate results.
4. What Are the Prompting Styles in LLMs?
When working with large language models like ChatGPT, LLaMA, or other AI systems, the way you write your prompt matters a lot. Different models are trained using different prompt formats or styles. These formats help the model understand what the user wants and how it should respond.
Below are four common prompting styles explained in clean, simple language.
- ALPACA Prompt Style
- INST Prompt Style
- FLAN Prompt Style
- Zero-shot Prompting
- Few-shot Prompting
- CHAT Prompt Style
1. ALPACA LLM Prompt Style
ALPACA style is used for training models with instruction-following examples.
It follows a fixed structure: Instruction + Input + Output Mostly used in research and fine-tuning datasets.
Structure
Instruction: <task>
Input: <data>
Response: <expected output>Prompt Example:
Instruction: Translate to Hindi
Input: "Good morning"
Response: "सुप्रभात"Why it’s used
- Helps when training or fine-tuning open-source LLMs
- Clear separation of instruction, input, and output
- Models learn exactly how to follow commands
2. INST LLM Prompt Style
INST means Instruction Style, used to directly tell the AI what to do, no extra formatting, no explanation.
It wraps the instruction inside [INST] ... [/INST] tags.
Structure
[INST] your instruction here [/INST]Prompt Example:
[INST] List 5 benefits of drinking water. [/INST]Output:
1. Improves digestion
2. Boosts skin health
3. Gives energy
4. Removes toxins
5. Maintains hydrationWhy it’s used
- Clean and simple
- Good for instruction-tuned models
- Model knows the task quickly
3. FLAN LLM Prompt Style
FLAN comes from Google’s FLAN models. It focuses on Zero-Shot and Few-Shot learning.
You usually give examples before the real task, so the model understands the pattern.
Few-Shot Example:
You are a helpful assistant.
Task: Translate English sentences into Hindi.
Example 1:
English: I am going to school.
Hindi: मैं स्कूल जा रहा हूँ।
Example 2:
English: What is your name?
Hindi: आपका नाम क्या है?
Now translate this:
English: The weather is very nice today.Output:
Hindi: आज मौसम बहुत अच्छा है।Zero-Shot Example:
Translate the following sentence to Hindi:
“It is raining heavily outside.”Output:
“बाहर बहुत तेज़ बारिश हो रही है।”Why it’s used
- Perfect for reasoning and translation
- Works well for problems with patterns
- Helps model understand context before task
4. CHAT LLM Prompt Style
CHAT style is used in chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini. And used widely in production AI systems.
It uses roles:
- System: sets the behaviour
- User: asks the question
- Assistant: gives the answer
- Developer (optional): hidden instructions for the model
Structure
System: Define AI role and behavior
User: Ask something
Assistant: Gives answer
Developer: (hidden instructions)Prompt Example:
System: You are a polite travel guide.
User: Suggest 3 places to visit in Delhi.
Assistant: (Gives list)The message format is shown as an array:
message = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a polite travel guide."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Suggest 3 places to visit in Delhi."
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "India Gate, Red Fort, Connaught Place"
}
]Why it’s used
- Makes conversation natural
- Helps control tone and personality
- Used in chatbots, agents, AI assistants
5. CHAT LLM Implementation Using Node.js
Chat Completion in Node.js
Using Node.js, you can send prompts to an AI model and receive responses using APIs like OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, DeepSeek, etc.
This is how modern chatbots, AI assistants, automation tools, and voice agents are built. Use this: https://platform.openai.com/docs/overview
Example Code:
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
messages: [
{ role: "user", content: "Who are you?" }
],
model: "claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
});
console.log(response.choices[0].message);This code sends a chat-style message to the LLM and receives the reply.
What is Cache Token?
A Cache Token means the AI model can reuse previously processed text instead of reprocessing everything from the beginning.
Simple Explanation: When you send a long prompt repeatedly, the model normally processes the full text again and again. But with cache tokens, the model stores the already processed part so it doesn’t repeat the work.
Why it matters
- Saves time (faster responses)
- Saves cost (fewer tokens used)
- Useful for long documents or long chats
Example for Cache Tokens
Without cache tokens: You send a 20-page document multiple times then the model re-reads all 20 pages every time.
With cache tokens: The model stores the processed part of those 20 pages and then next time it only works on new changes, not the whole document.
Think of it like AI saying, “I already remember this page, no need to read again”.
What is a Stateless API?
A Stateless API means the server does not remember anything from previous requests.
Every request is treated as new and separate.
Simple Explanation: The AI does not maintain chat history by itself. You MUST send the past messages again if you want the AI to continue the conversation.
Why it matters
- You control the conversation history
- Keeps API simple and scalable
- Makes data handling more secure
Example of Stateless API
You send this request:
User: Hello, My name is manojLater you send:
User: What is my name?The API will not understand this is the same conversation
unless YOU send both messages together as history:
[
{ role: "user", content: "Hello, My name is manoj" },
{ role: "user", content: "What is my name?" }
]In Simple Words: A Cache Token means AI remembers processed text (inside model) Stateless API means Server does NOT remember your previous messages (you must resend them)
6. System Prompting
System Prompting means setting the rules, personality, tone, and behavior of the AI before it starts responding.
Think of it like giving the AI a “job description” or “role” before the conversation begins.
Why is System Prompting important?
- It tells the AI how it should think
- It defines how formal or casual the AI should be
- It controls what style of answer the AI should give
- It helps avoid wrong or irrelevant responses
- It improves accuracy in reasoning tasks
Example of a System Prompt:
System: “You are a motivational coach who always speaks positively and clearly.”Now the AI will always answer in a positive and encouraging way.
Types of System Prompt Engineering
System prompting has 5 major techniques, each used for different situations.
1. Zero-Shot Prompting
Zero-Shot Prompting means:
- You give the AI a task without providing any examples
- The model must use its existing knowledge to answer
How it works
You tell the AI directly what to do, and it figures out the solution from its training.
Simple Example
You: “Translate ‘How are you?’ into French.”
AI: “Comment ça va ?”You gave no examples, yet the AI solved the task correctly.
Where it is useful
- Quick tasks
- When you trust the AI to know the topic
- When you need fast answers
- Any task that doesn’t require a special format
Why it works
Modern LLMs already have strong general knowledge, so they can handle many tasks without prior examples.
2. Few-Shot Prompting
Few-Shot Prompting means:
- You give the AI a few examples of the task
- Then you ask it to solve a new similar task
- The examples act like “training” within the prompt
The AI understands the pattern, not just the text.
Simple Example
You:
Example 1:
English: “Hello” in Spanish: “Hola”
Example 2:
English: “Goodbye” in Spanish: “Adiós”
Now you ask:
“English: Thank you in Spanish: ?”
AI: “Gracias”Where it is useful
- Custom formats
- Specific writing styles
- Tasks where model must follow a pattern
- Data extraction
- Resume or topic-specific tasks
- Complex formatting (e.g., JSON output)
Why it works
Examples act as a mini training dataset inside the prompt, the model learns how to format the answer.
Few-shot is one of the most powerful prompting methods.
3. Chain-of-Thought Prompting (CoT)
Also called Step-by-Step Reasoning or Judgmental Prompting.
You instruct the AI to:
- Explain how it reached the answer
- Break the solution into steps
- Think like a human, step-by-step
This improves accuracy, especially for reasoning problems.
Simple Example
You:
“A shop sells apples for $2 each. You buy 3 apples.
How much do you spend? Explain step-by-step.”
AI:
Step 1: Price of 1 apple = $2
Step 2: 3 apples × $2 = $6
Final Answer: $6Where it is useful
- Math problems
- Logical reasoning
- Coding explanations
- Complex decision-making
- Multi-step workflows
Why CoT is powerful
When the AI explains the steps, it reduces:
- Hallucinations
- Wrong assumptions
- Missing logic
It forces the model to think before answering. And use Perplexity for better understanding about COT prompting.
4. Self-Consistency Prompting
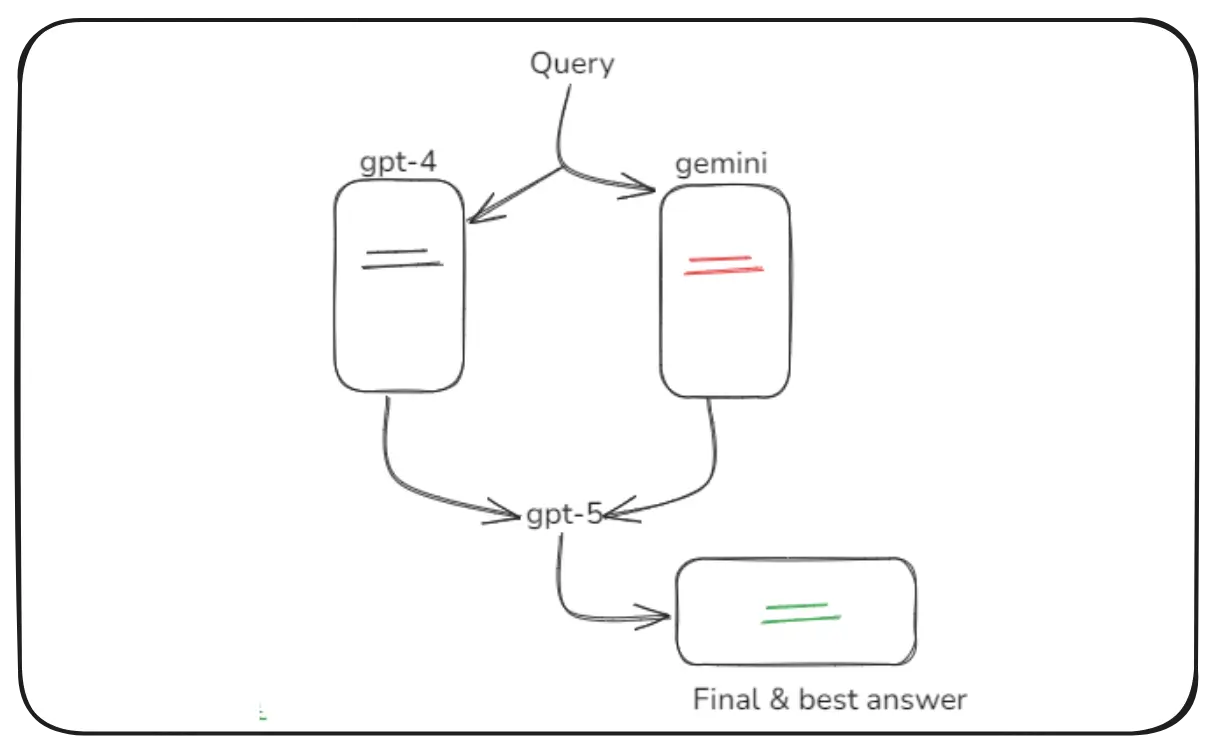
Self Consistency Prompting
Self-Consistency prompting means:
- The AI generates multiple reasoning paths
- It compares all paths
- It selects the most common or logical final answer
The model acts like a committee of experts debating before deciding.
Simple Example
You: “What is 25 × 4?”
AI internally tries different methods:
- Method 1: 25 + 25 + 25 + 25 = 100
- Method 2: 25 × 2 = 50 → 50 × 2 = 100
- Method 3: 20 × 4 = 80 → 5 × 4 = 20 → 80 + 20 = 100
Final Answer: 100 (Because it appears in all methods)Where it is useful
- High accuracy tasks
- Complex reasoning
- Reducing hallucination
- Confusing logic questions
Why it works
Instead of giving one answer directly, the AI:
- Checks multiple possibilities
- Compares them
- Chooses the best, most consistent one
It makes the result more reliable and less random.
5. Persona-Based Prompting
Persona Based Prompting is also called Personalization Prompting.
You tell the AI to act like a specific role, character, or personality.
The AI then answers in that character’s style.
Simple Example
You: “You are a friendly fitness coach. Give me a simple morning workout plan.”
AI: “Let’s begin with warm-up stretches, followed by 10 push-ups, 15 squats,
and a quick 5-minute jog!”Where it is useful
- Customer support agents
- Chatbots with personality
- Teachers or trainers
- Storytelling
- Marketing assistants
- Sales personas
- Role-playing simulations
Why it works
Persona instructions shape the model’s:
- Tone
- Speaking style
- Level of detail
- Emotional expression
It makes the AI feel more human-like and natural, and this technique is widely used by EdTech companies to create personalized learning experiences.
Conclusion
Mastering Prompt Engineering is essential for anyone working with Generative AI. By learning how to write clear, structured, and effective prompts, you can unlock the full potential of LLMs and build powerful AI applications.
Happy Learning and Building with Generative AI!